Fusion welding process in which coalescence is achieved by energy of a highly concentrated, coherent light beam focused on joint.
Laser Beam Welding (LBW)
Fusion welding process in which coalescence is achieved by energy of a highly concentrated, coherent light beam focused on joint
Laser = “light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation” LBW normally performed with shielding gases to prevent oxidation
Filler metal not usually added
High power density in small area, so LBW often used for small parts
Working
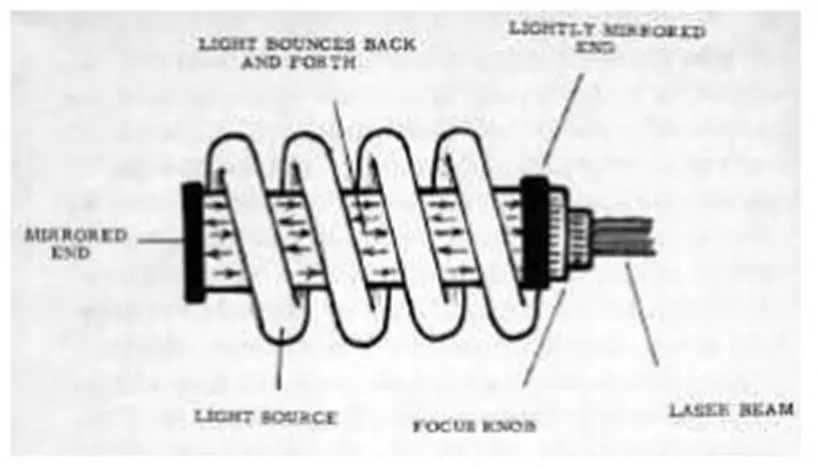
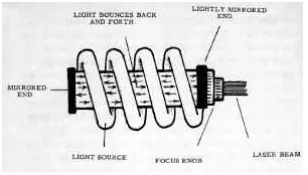
The laser WELDING system consists of a power source, a flash lamp filled with Xenon, lasing material, focusing lens mechanism and worktable. The flash tube flashes at a rate of thousands per second. As a result of multiple reflections, Beam power is built up to enormous level.
The output laser beam is highly directional and strong, coherent and unicromatic with a wavelength of 6934oA. It goes through a focusing device where it is pinpointed on the work piece, fusion takes place and the weld is accomplished due to concentrated heat produced. Laser beam welding process is shown in the figure.
Advantages.
1.Wide variety of metals can be welded. 2.Thermal damage is minimum.
3.Weld metal is purified.
4.Good ductility and mechanical properties. 5.Welds are vaccum tight.
6.filler metal is not used.
7.No effect on heat treated components.
Limitations.
1.Low welding Speed.
2.Limited to thickness of 1.5mm. 3.Materials like Mg cannot be welded.


Comments are closed.